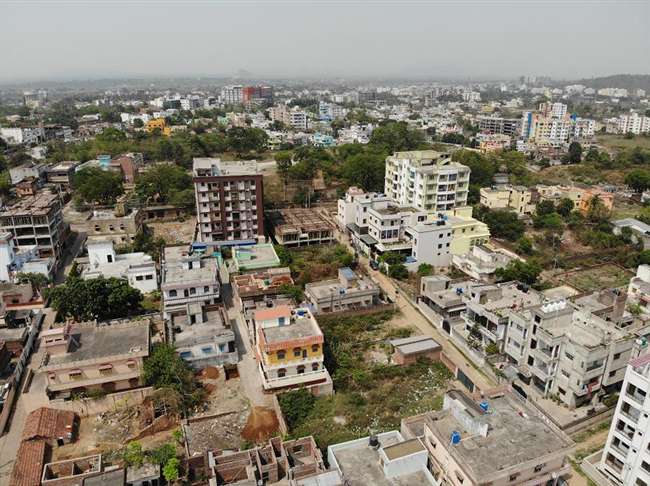
Dhanbad is the second-most populated city in the Indian territory of Jharkhand after Jamshedpur. It positions as the 42nd biggest city in India and is the 34th biggest million or more metropolitan agglomeration in India. Dhanbad imparts its property lines to the Paschim Bardhaman area and Purulia locale of West Bengal and Bokaro, Giridih and Jamtara regions of Jharkhand. The city knows as the ‘Coal Capital of India’ for lodging one of the biggest coal mineshafts in India. The lofty organization, Indian School of Mines (presently IIT Dhanbad) is arranged in Dhanbad Jharkhand. Aside from coal, it has additionally filled in data innovation.
Dhanbad is the 96th quickest developing city on the planet to the City Mayors Foundation. It is the 56th cleanest city in India, as per the 2019 Swachh Survekshan neatness review. It showed an extraordinary change in the city which view as the dirtiest city in the 2018 Swachh Survekshan. Dhanbad Municipal Corporation works for expanding green cover in the city.
धनबाद जमशेदपुर के बाद झारखंड के भारतीय क्षेत्र में दूसरा सबसे अधिक आबादी वाला शहर है। यह भारत के 42वें सबसे बड़े शहर के रूप में स्थित है और भारत में 34वां सबसे बड़ा मिलियन या अधिक महानगरीय समूह है। धनबाद पश्चिम बर्धमान क्षेत्र और पश्चिम बंगाल के पुरुलिया लोकेल और झारखंड के बोकारो, गिरिडीह और जामताड़ा क्षेत्रों में अपनी संपत्ति लाइन प्रदान करता है। भारत में सबसे बड़ी कोयला खदानों में से एक को दर्ज करने के लिए शहर को ‘भारत की कोयला राजधानी’ के रूप में जाना जाता है। धनबाद में प्रतिष्ठित संगठन, इंडियन स्कूल ऑफ माइन्स (वर्तमान में IIT धनबाद) की व्यवस्था की गई है। कोयले के अलावा इसने डाटा इनोवेशन भी भरा है।
History:
The current locale used to be a piece of the Manbhum district and was involved by Mundari tribals in the wild of South unified Bihar. In the seventh century A.D., some data is accessible from the record of the movements of Hieun Tsang. These records portray the presence of a strong realm which included the locale and connecting regions, controlled by Sasanka. Manbhum was one of the areas of East India during the British Raj.
Also Read: Bhulekh Jharkhand, Highlights of Jharbhumi, How to Che…Read More.

The district has thick timberlands, with rich mineral assets, and had a blended segment profile in with individuals from various strict gatherings, including Adivasis, especially the Santals and the Mundas before the city was laid out. After the Partition of India, the locale turned into a piece of Bihar state, and upon re-association of the Indian states during the 1950s, the region turned into a piece of West Bengal. The Purulia area was cut out of the region of Manbhum.
वर्तमान स्थान मानभूम जिले का एक टुकड़ा हुआ करता था और दक्षिण एकीकृत बिहार के जंगल में मुंडारी आदिवासियों द्वारा शामिल किया गया था। सातवीं शताब्दी ईस्वी में, ह्वेन त्सांग के आंदोलनों के रिकॉर्ड से कुछ आंकड़े उपलब्ध हैं। ये रिकॉर्ड एक मजबूत क्षेत्र की उपस्थिति को चित्रित करते हैं जिसमें सासांका द्वारा नियंत्रित स्थानीय और कनेक्टिंग क्षेत्र शामिल हैं। ब्रिटिश राज के दौरान मानभूम पूर्वी भारत के क्षेत्रों में से एक था।
Geology:
Dhanbad has a typical height of 227 m (745 ft). Its geological length (reaching out from north to south) is 15 miles (24 km) and its broadness (extending across east to West) is 10 miles (16 km). It imparts its limits to West Bengal in the eastern and southern part, Dumka and Giridih in the North and Bokaro District in the west. Dhanbad goes under the Chota Nagpur Plateau.
Waterways and Lakes:
The Damodar is a significant stream of the Chota Nagpur Plateau. It ascends in Palamu and streams toward the east between the levels of Ranchi and Hazaribag. It joins the Bokaro, the Konar and the Barakar waterways. The Damodar enters the Dhanbad locale in conjunction with the Jamuria, a stream which denotes the western limit of Dhanbad with the Hazaribagh District. Further east, the Damodar join by the Katri River which ascends in the lower regions underneath Parasnath and crosses through the coal-field region. The Barakar, which shapes the northern limit of the region, crosses around 77 km. It streams in the south-westerly bearing up to Durgapur and afterwards south till it joins the Damodar close to Chirkunda.
Also Read: MGNREGA Jharkhand, How to Check Job Card List, Local…Read More.
Environment:
Dhanbad highlights an environment that is temporary between a moist subtropical environment (Köppen: Cwa) and a tropical wet and dry environment (Aw). Summer begins from the last seven-day stretch of March and finishes in mid-June. The pinnacle temperature in summer can reach 48 °C. Dhanbad additionally gets weighty precipitation. In winter, the base temperature stays around 10 °C with a limit of 22 °C.
Useful Links:
Job Application, Free Computer Institute Registration in India, Computer Courses Franchise in India, Computer Centre Franchise in India, Computer Centre Franchise Opportunity in India.

Socioeconomics:
Population:
As of the 2011 registration, Dhanbad City had a populace of 1,162,472. Guys (614,722) comprise 53% of the populace and females (547,750) 47%. It has a sex proportion of 891. Dhanbad has a typical proficiency pace of 79.47%, higher than the public normal of 74.04%: male education is 86.14% and female proficiency is 71.96%. 10.57% of the populace is under 5 years old.
Religion:
Hinduism is the prevailing religion with more than 81% followers. The minority religions are Islam, Sikhism and Christianity.
Also Read: Aahar Jharkhand PDS, What is PDS, Benefits of Ration Car…Read More.
Economy:
Dhanbad has one of the most established and biggest business sectors in the district and is likewise a focal point of huge scope enterprises. It knows for its coal mineshafts and modern foundations; the city is encircled by around 112 coal mineshafts with a complete creation of 27.5 million tons and a yearly pay of 7,000 million rupees through the coal business. There are various coal washeries there.
Transport:
Rail:
Dhanbad has a generally excellent rail network with the other significant pieces of the country, for example, Delhi, Mumbai, Patna, Kolkata, Bhagalpur, Munger, Gaya, Chennai, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad, Kochi, Indore, Bhopal, Gwalior, Jabalpur, Jaipur, Visakhapatnam Jodhpur, Nagpur, Pune, Varanasi, Guwahati and Bangalore and so on. Dhanbad rail line division is the second biggest income generator in India after Mumbai Rail Division.
Roads:
Public Highway 19 and National Highway 18 are the significant roadways going through Dhanbad. NH 19 is essential for the Golden Quadrilateral (GQ) expressway organization; Dhanbad lies in the Kolkata-Delhi connection of the Golden Quadrilateral organization. NH19 changed over into a six-path turnpike; NH 18 interfaces Dhanbad to Bokaro-Jamshedpur. Private and State transports are accessible between city travel.

FAQs on Dhanbad Jharkhand:
Where could Bhatinda Waterfall be?
Bhatinda Falls has situated a good way off only 14 km from Dhanbad Railway Station. The cascades make an ideal outing spot for some individuals. It settled amid vegetation and rough slopes. It gives an all-encompassing perspective to nature sweethearts.
For what reason is Dhanbad well known?
This city is well known in India in the field of coal mining. Many rumoured modern, social, social and different organizations view here. Therefore trade here is extremely wide. Dhanbad, situated in Jharkhand, is otherwise called the coal capital of India.
Also Read: Jharkhand Police Vacancy 2022, Eligibility, Application Fee…Read More.
What was the old name of Dhanbad?
In 1965, Dhanbad was cut out of the Manbhum region and made a locale. Therefore leftover pieces of Manbhum stayed in West Bengal, which came to know as the Purulia area.
What number of coal mineshafts are there in Dhanbad?
Dhanbad has the absolute biggest coal mineshafts in India and knows as the coal capital of India. The city is encircled by ~112 coal mineshafts with an all-out creation of 27.5 million tons.
Useful Links:
Business Ideas Pune, Hello Mobile, Gram Panchayat List, Jamshedpur Jharkhand, Bestie Meaning in Hindi.